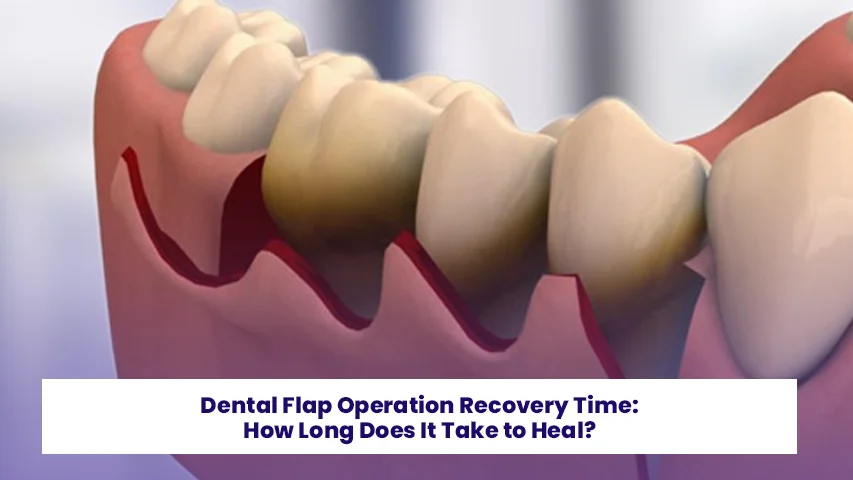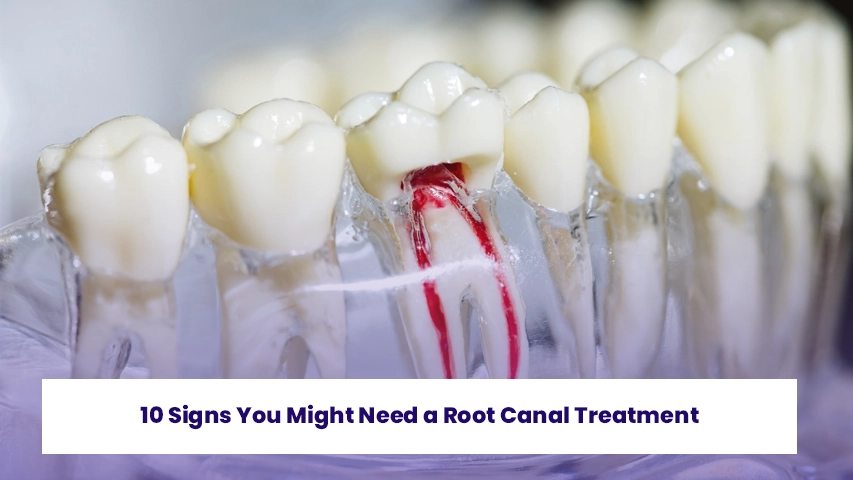
Can an Infected Tooth Be Extracted? Abscessed Tooth Extraction and Treatment Methods
21 February 2025
What actually is Smile Design? How is Smile Design Done?
25 March 2025Tooth Sensitivity: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Tooth sensitivity is quite a general problem for many people which tends to make eating, drinking, and sometimes even breathing difficult. The most problematic one is when the inner areas of teeth become exposed, which causes stinging aches when interacting with particular food, liquids, or temperature. If you have ever bitten something hot or cold and suddenly felt pain in your teeth, then you may have already gone through this very type of pain. What it is, symptoms to look out for, how to prevent it, and what can treat it will be elaborated on in this article.
What is Sensitivity of Teeth?
Teeth sensitivity is identified as dentin hypersensitivity, which is a state where teeth become extremely sensitive to stimuli such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic food or drinks.
Its outer hard layer, enamel, is destroyed, exposing both the hard and soft components of the tooth in dentin. The tiny nerve fibers are stimulated and induce pain when activated. This is a common cause of tooth sensitivity and could either be temporary or permanent depending on the cause. Sometimes sharp pain spoils the joy of mere activities like the drinking of coffee, the eating of ice creams, or even tooth brushing. In its first occurrence, it is likely to be interpreted to mean that the guard of the tooth has been lost and the nerves have been exposed to the outside world. If not treated, sensitivity can slowly worsen to more severe dental problems, and hence detection and treatment of the reason early on is vital.
What Causes Tooth Sensitivity?
There are several causes for sensitive teeth, and the most commonly known ones are the gradual wearing off of tooth enamel. The enamel is gradually worn away due to numerous causes such as ingestion of acidic foodstuffs and drinks, heavy brushing, or bruxing. If this is the reason, it will expose the underlying dentin which is much more sensitive to heat and certain food items.
One of the most common tooth sensitivity causes is gum recession. When gums pull back from teeth, they expose roots, which do not have an enamel layer to cover them. Thus, their exposure makes them more sensitive. Decay or a cavity that creates holes in teeth and thus offers avenues for external factors to enter and affect nerves, leading to a strong response, is another potential reason. Also, teeth chips or cracks easily expose the sensitive inner layers, leading to pain.
Sometimes, sensitivity is a temporary symptom associated with some forms of dental treatment such as cleaning, filling, or whitening. However, if the sensation persists despite treatment, it may be a sign of something more serious that needs further help. Tooth sensitivity causes need to be detected early so that they can be treated and prevented from developing into more serious dental issues.
Common Symptoms of Sensitive Teeth
Any susceptibility to tooth sensitivity signs may cause varied manifestations. Sharply pinching pain may occur upon consumption of anything sweet or acidic. This pinching kind of discomfort could stop almost instantly upon relieving the painful stimulating factor; in a different context, it may resolve anywhere in a frame between two to three minutes upon stopping the stimulus. This sensation can even prevent you from eating or drinking your favorite foods or beverages because they violate the rules of normal eating and drinking.
Plus, one more sign hinges on extreme sensitivity when flossing or brushing. If you have a feeling that your teeth are hurting while brushing at the gum line, this can be a warning that the tooth is sensitive. Other sources of sensitivity are gum recession, which exposes the root of your tooth and would feel cold air entering your mouth as if it were stabbing you, specifically for incomplete teeth. Some people would feel the discomfort of inhaling cold air, especially when their teeth are exposed or damaged. If any of these symptoms of tooth sensitivity describe you, especially if they happen routinely, then you must seek an evaluation for your teeth, and sensitivity should be addressed on an urgent basis before it increases.
If you experience any of these symptoms of tooth sensitivity, it is important to act quickly, as the condition left untreated can lead to more pain and complications.
Foods and Drinks That Trigger Sensitivity
Certain foods have been known to activate or worsen sensitivity in the teeth. Cavite stretching gums tend to pull back from the enamel. Acidic foodstuffs, wherein citrus fruits, tomatoes, and vinegar based dressings aggravate sensitive teeth, are a common culprit. These acids erode the already thin enamel, making them more susceptible to hot and cold sensitivity in teeth, as well as any other stimulus. Instant and acute discomfort of teeth is caused by hot and cold drinks, including coffee, tea, and cold water. People with sensitive teeth would be pretty uncomfortable drinking such beverages, especially when they’re experiencing very hot or cold temperatures, which trigger hot and cold sensitivity in teeth.
Cavity causing bacteria grow a lot more on sugary snacks and leave their host with an aggravation of tooth sensitivity. Yes, and sugar can cause further damage to the enamel by contributing to the development of bacteria within the mouth that causes cavities and further damage to the enamel. Another classic culprit: soft drinks of the fizzy variety—soda—they boast acids and sugars which corrode the enamel quite speedily. Sticky foods such as caramel or chewing gum stick to teeth and lead to a greater cavity risk, exposing the sensitive areas of the tooth and worsening hot and cold sensitivity in teeth.
It thus becomes more important to refrain from consumption of such foods and beverages, if not completely, restrict it from being consumed in. After one has eaten a food item that is most likely to cause sensitivity, he or she ought to gargle with water as a precautionary measure to neutralize any acids and also minimize risks of irritation.
How to Prevent Tooth Sensitivity?
To reduce sensitivity, good oral cleaning habits and knowledge of habits that wear enamel are effective preventives to undertake. A few ways to base your preventive measures are by choosing the right toothbrush: a soft bristled one; brushing without force will combat tooth surface wear. Hard brushing with rapid strokes in circular motions may wear down the enamel in the teeth over time and cause receding. Brushing with a circular motion rather than backwards and forwards also helps protect the tooth surface.
Another preventive measure you may take is to use sensitive toothpaste. Sensitivity tooth pastes are great pain relief as they contain certain chemicals that defend against pain from dental nerves in the teeth. Fluoride toothpaste also works by strengthening enamel and protecting against decay.
In addition, you could protect enamel by limiting acidic foods and drinks. Less consumption of these types of items, citrus fruits, sodas, and vinegar foods will mean less wear on the surface of the tooth. It can also protect teeth from serious grinding by wearing a mouthguard while sleeping. Over time, regular dental visits can identify early signs of tooth decay, periodontitis, or tooth erosion and offer timely solutions.
These measures and precautions would go a long way in ensuring that you do not walk around with throbbing teeth, while still giving you that lovely smile.
Best Treatments for Sensitive Teeth
When tooth sensitivity becomes chronic, there are several treatments available for relief. One commonly used treatment is desensitizing toothpaste. Such toothpaste contains specific compounds that act on the pathways to the dental nerves, reducing sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli. Regular use of this type of toothpaste is thus required to achieve full benefits.
Another factor in treating the patient’s dental discomfort would be fluoride treatments. Fluoride strengthens the teeth upon application and makes the enamel more resistant to decay and less prone to discomfort. Often, the dentist will be performing these treatments with the patient during the regular appointment. Dental bonding may sometimes be required to cover the exposed areas of the tooth. Basically, it means applying a tooth-colored resin to the area and forming a protective barrier to reduce sensitivity.
If sensitivity becomes deep rooted, a root canal may be suggested by the dentist for appropriate treatment. It is a method of treatment that will eliminate the infected or damaged tissue present in the tooth, hence eradicating the cause of discomfort. Another procedure to prevent chewing surfaces from being sensitive is to apply a dental sealant, as advised by the dentist.
For those who experience persistent discomfort, a consultation with a dentist specializing in tooth sensitivity treatments can determine the best solution. There are several tooth sensitivity treatments, and the best treatment will depend on the sensitivity level as well as the underlying cause.
When to See a Dentist for Tooth Sensitivity?
Teeth sensitivity can be minimal in most patients and can be treated at home using over the counter products. In certain situations, however, not only is it recommended that one see the dentist, but it is required. Acute presentation of sensitivity could indicate more advanced oral pathology, such as cavities or periodontal disease. If the sensitivity hurts or if the hurting is affecting your daily life, then it is advisable to see a professional for dental treatment. You should also check the teeth for cracks and chips, since they will deteriorate and lead to sensitivity, and see a dentist as early as possible for proper dental treatment. When you have receding gums or any other symptoms of gum disease, the dentist may prescribe dental care that will cure them and desensitize you.
Otherwise, if the pain is not soothed with home remedies, an appointment should be made with the dentist. We will help find the cause of the pain and administer much needed relief treatment.
It can be handled and alleviated in the proper way. Learn something, recognize its symptoms and signs, and take preventative measures for it. If the pain is chronic, professional care would provide long term relief and avoid further wear on your teeth. Acting early on means you will be able to eat and drink anything you want without any discomfort.